Spring Boot
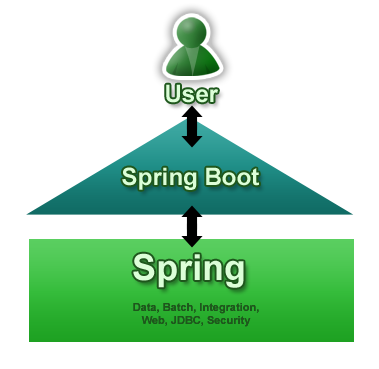
What's Spring Boot
- Spring Boot is not a framework to write applications, it helps you to build packages and reply the Spring application with minimal or absolutely no configuration
- Create stand-alone Spring applications
- Spring Boot add default opinionated configuration out of the box
- Web Application can be delivered as a FAT-JAR file to run as stand alone application
What's Spring Boot
Why We Need Spring Boot?
- Stand-alone Spring applications
- Embedded Tomcat or Jetty
- Starter dependencies
- Automatic configuration
- Production-ready environment
- Convention over configuration
- No code generation / no XML config
Getting started with Spring Boot
“Spring Boot project is just a regular Spring project that happens to leverage Spring Boot starters and auto-configuration”
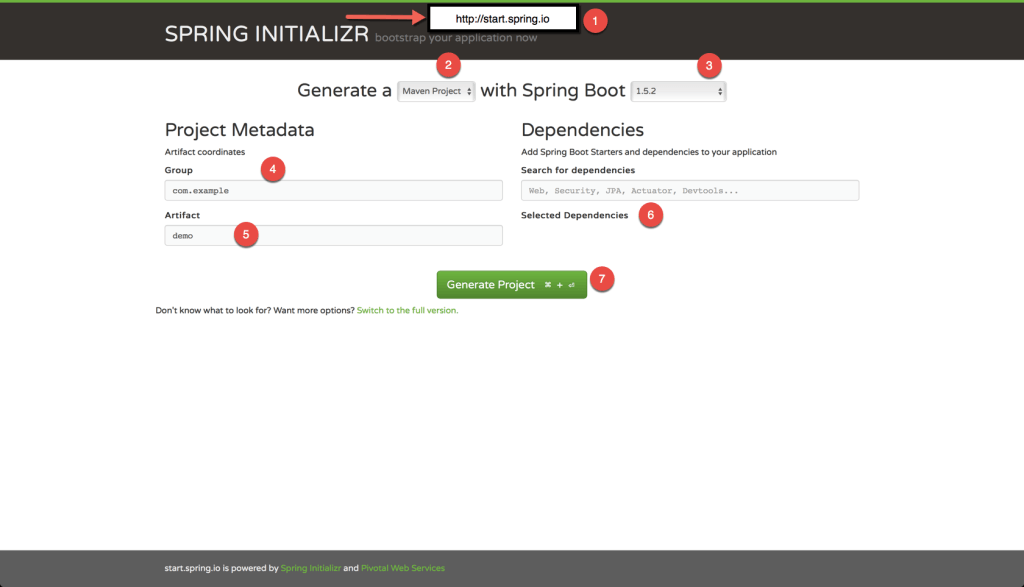
Initializing a Spring Boot project with Spring Initializr
Using spring initializr’s web interface
Project structure

Developing your first Spring Boot application
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}
The @SpringBootApplication enables Spring component-scanning and Spring Boot auto-configuration
@SpringBootApplication combines three other useful annotations @Configuration, @ComponentScan, @EnableAutoConfiguration
Build & Run
$ gradle bootRun
The bootRun task comes from Spring Boot’s Gradle plugin. Alternatively, you can build the project with Gradle and run it with java at the command line
$ gradle build
...
$ java -jar build/libs/firstApp-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
Spring Boot project build
buildscript {
ext {
springBootVersion = '1.5.6.RELEASE'
}
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
classpath("org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-gradle-plugin:${springBootVersion}")
}
}
apply plugin: 'java'
apply plugin: 'eclipse'
apply plugin: 'org.springframework.boot'
jar {
baseName = 'SampleSpringBoot'
version = '0.0.1-SNAPSHOT'
}
sourceCompatibility = 1.8
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
dependencies {
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-aop')
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-web')
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa')
runtime('com.h2database:h2')
testCompile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test')
}
Spring Restful Annotations
@RestController
Defines the class as a Spring Restful controller
@RestController
public class HelloWorldController {
}
@RequestMapping
Define URL mapping for a class and/or method
@RestController
public class HelloWorldController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/helloWorld", method = { RequestMethod.GET })
public String helloWorld() {
return "helloWorld";
}
}
@RequestMapping(cont.)
Arguments and return types
@RestController
public class SomeController {
@RequestMapping(value = "/pets", method=RequestMethod.POST)
public Pet addPet(@RequestBody Pet pet) {
// implementation omitted
return someObj;
}
}
- String - Return value
- someMethod - Arguments
Allowed arguments
- HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse, HttpSession
- java.util.Locale
- java.io.InputStream, java.io.Reader
- java.io.OutputStream, java.io.Writer
- java.security.Principle
- HttpEntity
- java.util.Map, Model, ModelMap
- Errors, BindingResult
- etc.
Allowed return types
- ModelAndView, Model, java.util.Map, View
- String
- Represents a view name, if not specified otherwise.
- void
- HttpEntity, ResponseEntity
- etc.
@PathVariable
In Spring MVC use the @PathVariable annotation on a method argument to bind it to the value of a URI template variable
@RequestMapping(value="/owners/{ownerId}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String findOwner(@PathVariable String ownerId, Model model) {
// implementation omitted
}
or
@RequestMapping(value="/owners/{ownerId}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String findOwner(@PathVariable("ownerId") String theOwner) {
// implementation omitted
}
@PathVariable(cont)
A method can have any number of @PathVariable annotations
@RequestMapping(value="/owners/{ownerId}/pets/{petId}", method=RequestMethod.GET)
public String findPet(@PathVariable String ownerId, @PathVariable String petId) {
// implementation omitted
}
eg.
http://www.example.com/owners/42/pets/21
@RequestParam
Use the @RequestParam annotation to bind request parameters to a method parameter in controller
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/pets")
public class PetController{
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.GET)
public Pet setupForm(@RequestParam("petId") int petId) {
Pet pet = this.clinic.loadPet(petId);
return pet;
}
}
***Parameters using this annotation are required by default
e.g., @RequestParam(value="id", required=false)
@RequestBody
Indicates that a method parameter should be bound to the value of the HTTP request body
@RequestMapping(value = "/something", method = RequestMethod.PUT)
public void handle(@RequestBody String body {
// implementation omitted
}
@ResponseBody
Indicates that the return type should be written straight to the HTTP response body
@RequestMapping(value = "/something", method = RequestMethod.GET)
@ResponseBody
public String helloWorld() {
return "Hello World";
}
H2
“H2 is a relational database management system written in Java. It can be embedded in Java applications or run in the client-server mode.”
Dependencies
dependencies {
runtime('com.h2database:h2')
}
Configuration H2
Add configuration in application.properties
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:~/springboot;DB_CLOSE_ON_EXIT=FALSE
spring.jpa.database-platform=H2
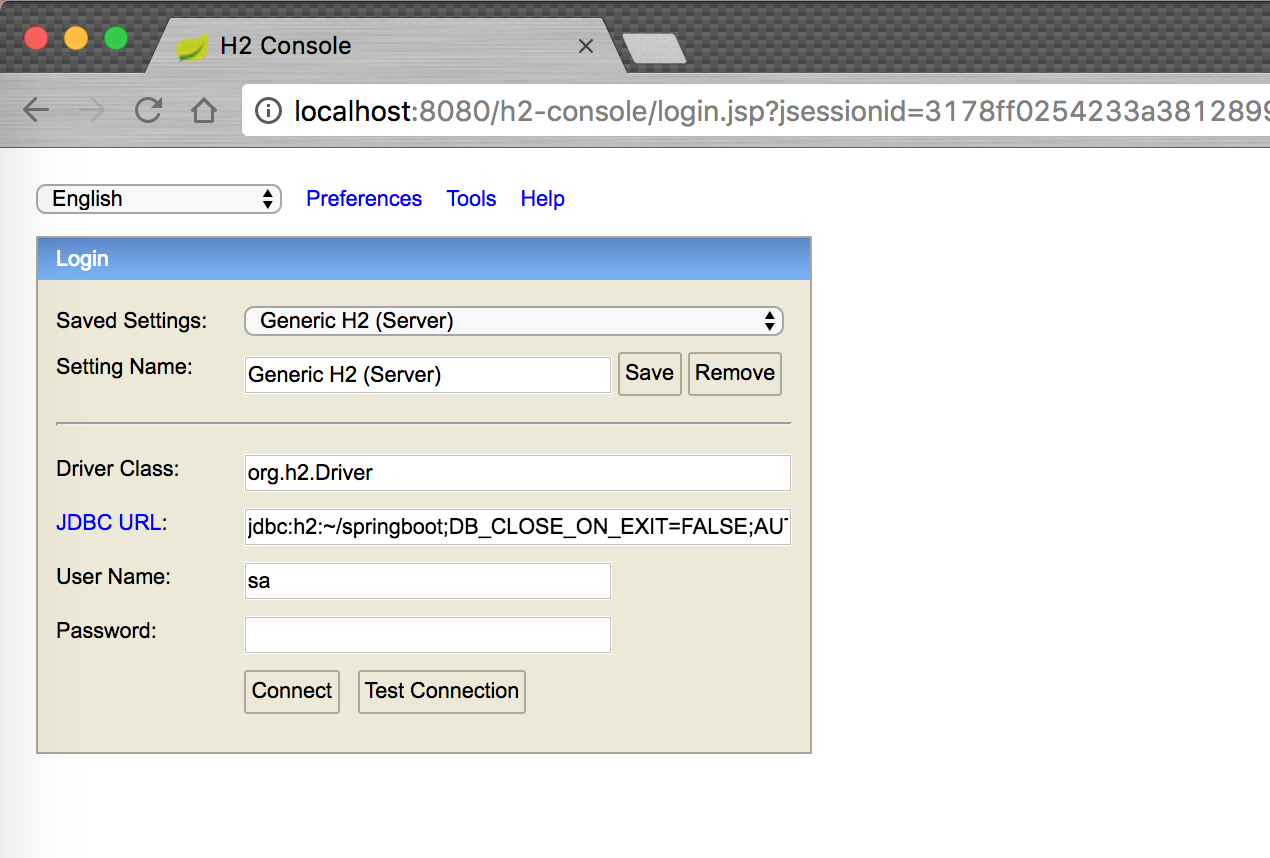
Enable Server Mode
Update configuration AUTO_SERVER=TRUE
spring.h2.console.enabled=true
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:h2:~/springboot;DB_CLOSE_ON_EXIT=FALSE;AUTO_SERVER=TRUE;
spring.jpa.database-platform=H2
Loading data using SQL script
update application.properties
spring.datasource.platform:h2
create file data-h2.sql in /src/main/resources/data-h2.sql
insert into employee (first_name, last_name) values ('john', 'doe');
insert into employee (first_name, last_name) values ('james', 'doe');
insert into employee (first_name, last_name) values ('smith', 'doe');
insert into employee (first_name, last_name) values ('Assanai', 'Manurat');
enable configuration to enable spring boot execute script
spring.datasource.initialize=true
Loading data using programmatic
TRY...
Connect H2 Console
Data Access
Domain
@Entity
public class Employee {
@Id
@GeneratedValue
private Integer id;
private String firstName;
private String lastName;
public Integer getId() { return id; }
public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; }
public String getFirstName() { return firstName; }
public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; }
public String getLastName() { return lastName; }
public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; }
}
JPA Repository
@Repository
@Transactional(readOnly = true)
public class EmployeeRepository {
@PersistenceContext private EntityManager entityManager;
public List<Employee> findAll() {
Query query = entityManager.createQuery("from Employee");
return query.getResultList();
}
public Employee findById(Integer id) {
return entityManager.find(Employee.class, id);
}
}
Spring JPA Name Query
public Employee findByLastName(String lastName) {
Query query = entityManager.createQuery("from Employee e where e.lastName = :LAST_NAME");
query.setParameter("LAST_NAME", lastName);
List resultList = query.getResultList();
return resultList.isEmpty()? null : (Employee) resultList.get(0);
}
Spring JPA Native Query
public List<Employee> findAllByNativeQuery() {
Query nativeQuery = entityManager.createNativeQuery("select id, first_name, last_name from employee", Employee.class);
return nativeQuery.getResultList();
}
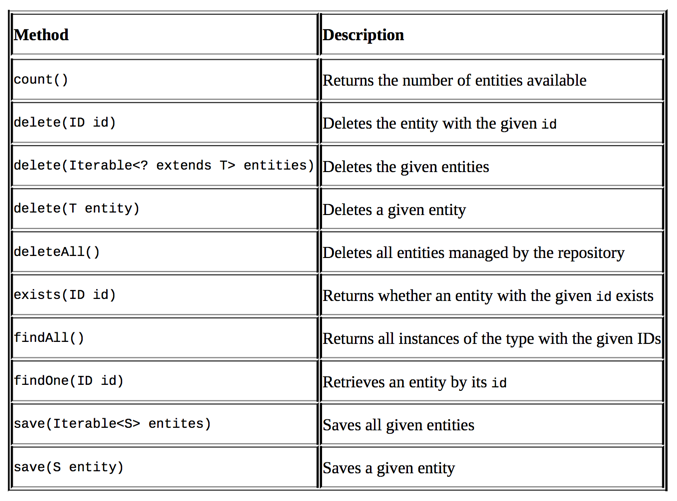
Spring Data Repository
Spring Data Repository
public interface EmployeeCrudRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> {
}
Spring Data Repository (Continue)
public interface EmployeeCrudRepository extends JpaRepository<Employee, Integer> {
List<Employee> findByFirstName(String firstName);
List<Employee> findByFirstNameAndLastName(String firstName, String lastName);
}
Initialize Execute Script
Create file data.sql in classpath
insert into employee (first_name, last_name) values ('john', 'doe');
insert into employee (first_name, last_name) values ('james', 'doe');
insert into employee (first_name, last_name) values ('smith', 'doe');
insert into employee (first_name, last_name) values ('Assanai', 'Manurat');
Testing
Dependencies
dependencies {
compile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-jpa')
runtime('com.h2database:h2')
testCompile('org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-test')
}
How to Write Unit Test
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class EmployeeControllerMockitoUnitTest {
private MockMvc mockMvc;
@InjectMocks
private EmployeeController controller = new EmployeeController();
@Mock
private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@Before
public void setup() {
MockitoAnnotations.initMocks(this);
// this.controller.setEmployeeRepository(employeeRepository);
this.mockMvc = MockMvcBuilders.standaloneSetup(controller).build();
}
@Test
public void getEmployeesShouldReturnListOfEmployees() throws Exception {
List<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<>();
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(1);
employee.setFirstName("john");
employee.setLastName("doe");
employees.add(employee);
BDDMockito.given(employeeRepository.findAll()).willReturn(employees);
this.mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/employees"))
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print())
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$", hasSize(1)))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.[0].id", equalTo(1)))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.[0].firstName", equalTo("john")))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.[0].lastName", equalTo("doe")))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk());
}
}
How to Write Unit Test (2)
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
@WebMvcTest(EmployeeController.class)
public class EmployeeControllerUnitTest {
@Autowired private MockMvc mockMvc;
@MockBean private EmployeeRepository employeeRepository;
@Test
public void testListEmployeeShouldReturnListOfEmployees() throws Exception {
List<Employee> employees = new ArrayList<>();
Employee employee = new Employee();
employee.setId(1);
employee.setFirstName("john");
employee.setLastName("doe");
employees.add(employee);
BDDMockito.given(employeeRepository.findAll()).willReturn(employees);
this.mockMvc.perform(MockMvcRequestBuilders.get("/employees"))
.andDo(MockMvcResultHandlers.print())
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$", Matchers.hasSize(1)))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.[0].id", Matchers.equalTo(1)))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.[0].firstName", Matchers.equalTo("john")))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.jsonPath("$.[0].lastName", Matchers.equalTo("doe")))
.andExpect(MockMvcResultMatchers.status().isOk());
}
}
Profile
Configuration Profile
@Profile("dev")
@Service
public class HelloService {
public String sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello, develop profile");
}
}
@Profile("production")
@Service
public class HelloService {
public String sayHello() {
System.out.println("Hello, production profile");
}
}
Set Active Profile
Add configuration in application.properties
spring.profiles.active=dev
Customizing configuration
Externalizing configuration with properties
$ java -jar SampleSpringBoot-1.0-SNAPSHOT.jar
--server.port=8000 --spring.profiles.active=dev